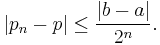Bisection method
The bisection method in mathematics is a root-finding method which repeatedly bisects an interval and then selects a subinterval in which a root must lie for further processing. It is a very simple and robust method, but it is also relatively slow. Because of this, it is often used to obtain a rough approximation to a solution which is then used as a starting point for more rapidly converging methods.[1] The method is also called the binary search method[2] and is similar to the computer science Binary Search, where the range of possible solutions is halved each iteration.
Contents |
The method
The method is applicable when we wish to solve the equation f(x) = 0 for the real variable x, where f is a continuous function defined on an interval [a, b] and f(a) and f(b) have opposite signs. In this case a and b are said to bracket a root since, by the intermediate value theorem, the f must have at least one root in the interval (a, b).
At each step the method divides the interval in two by computing the midpoint c = (a+b) / 2 of the interval and the value of the function f(c) at that point. Unless c is itself a root (which is very unlikely, but possible) there are now two possibilities: either f(a) and f(c) have opposite signs and bracket a root, or f(c) and f(b) have opposite signs and bracket a root. The method selects the subinterval that is a bracket as a new interval to be used in the next step. In this way the interval that contains a zero of f is reduced in width by 50% at each step. The process is continued until the interval is sufficiently small.
Explicitly, if f(a) and f(c) are opposite signs, then the method sets c as the new value for b, and if f(b) and f(c) are opposite signs then the method sets c as the new a. (If f(c)=0 then c may be taken as the solution and the process stops.) In both cases, the new f(a) and f(b) have opposite signs, so the method is applicable to this smaller interval.[3]
Analysis
The method is guaranteed to converge to a root of f if f is a continuous function on the interval [a, b] and f(a) and f(b) have opposite signs. The absolute error is halved at each step so the method converges linearly, which is comparatively slow.
Specifically, if p1 = (a+b)/2 is the midpoint of the initial interval, and pn is the midpoint of the interval in the nth step, then the difference between pn and a solution p is bounded by[4]
This formula can be used to determine in advance the number of iterations that the bisection method would need to converge to a root to within a certain tolerance.
Pseudocode
The method may be written in Pseudocode as follows:[5]
INPUT: Function f, endpoint values a, b, tolerance TOL, maximum iterations NMAX
CONDITIONS: a < b, either f(a) < 0 and f(b) > 0 or f(a) > 0 and f(b) < 0
OUTPUT: value which differs from a root of f(x)=0 by less than TOL
N ← 1
While N ≤ NMAX { limit iterations to prevent infinite loop
c ← (a + b)/2 new midpoint
If (f(c) = 0 or (b – a)/2 < TOL then { solution found
Output(c)
Stop
}
N ← N + 1 increment step counter
If sign(f(c)) = sign(f(a)) then a ← c else b ← c new interval
}
Output("Method failed.") max number of steps exceeded
See also
- Secant method
- Newton's method
- Root-finding algorithm
- Binary search algorithm
- Lehmer-Schur algorithm, generalization of the bisection method in the complex plane
- Nested intervals
- Brent's method
References
- Burden, Richard L.; Faires, J. Douglas (1985), "2.1 The Bisection Algorithm", Numerical Analysis (3rd ed.), PWS Publishers, ISBN 0-87150-857-5.
- Corliss, George (1977), "Which root does the bisection algorithm find?", SIAM Review 19 (2): 325–327, doi:10.1137/1019044, ISSN 1095-7200.
- Kaw, Autar; Kalu, Egwu (2008), Numerical Methods with Applications (1st ed.). http://numericalmethods.eng.usf.edu/topics/textbook_index.html
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Bisection" from MathWorld.
- [1] Java code by Behzad Torkian
- Bisection Method Notes, PPT, Mathcad, Maple, Matlab, Mathematica from Holistic Numerical Methods Institute
- Module for the Bisection Method by John H. Mathews